
Artificial intelligence and machine learning produce many of the advancements we see in the technology industry today. But how are machines given the ability to learn? Furthermore, how does the way we do this result in unintended consequences?
Here’s our quick explainer on how machine learning algorithms work, along with some examples of machine learning gone awry.
What Are Machine Learning Algorithms?
Machine learning is a branch of computer science that focuses on giving AI the ability to learn tasks. This includes developing abilities without programmers explicitly coding AI to do these things. Instead, the AI is able to use data to teach itself.
Programmers achieve this through machine learning algorithms. These algorithms are the models on which an AI learning behavior is based. Algorithms, in conjunction with training datasets, enable AI to learn.
An algorithm usually provides a model that an AI can use to solve a problem. For example, learning how to identify pictures of cats versus dogs. The AI applies the model set out by the algorithm to a dataset that includes images of cats and dogs. Over time, the AI will learn how to identify cats from dogs more accurately and easily, without human input.
Machine learning improves technology such as search engines, smart home devices, online services, and autonomous machines. It’s how Netflix knows which movies you’re more likely to enjoy and how music streaming services can recommend playlists.
But while machine learning can make our lives much easier, there can also be some unexpected consequences.
7 Times When Machine Learning Went Wrong
1. Google Image Search Result Mishaps
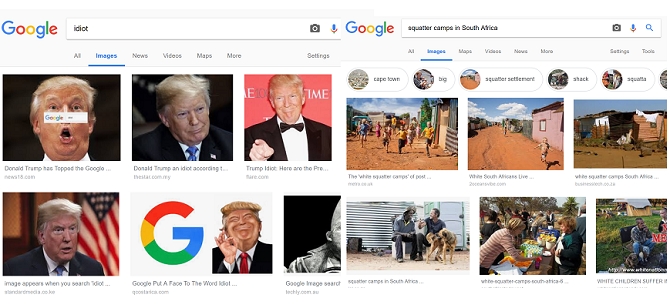
Google Search has made navigating the web a whole lot easier. The engine’s algorithm takes a variety of things into consideration when churning up results, such as keywords and bounce rate. But the algorithm also learns from user traffic, which can cause problems for search result quality.
Nowhere is this more apparent than in image results. Since pages that receive high traffic are more likely to have their images displayed, stories that attract high numbers of users, including clickbait, are often prioritized.
For example, the image search results for “squatters camps in South Africa” caused controversy when it was discovered that it predominately featured white South Africans. This is despite statistics showing that the overwhelming majority of those living in informal housing, such as shacks, are black South Africans.
The factors used in Google’s algorithm also means that internet users can manipulate results. For example, a campaign by users influenced Google Image Search results to the extent that searching for the term “idiot” shows images of US President Donald Trump.
2. Microsoft Bot Turned Into a Nazi
Trust Twitter to corrupt a well-meaning, machine-learning chatbot. This is what happened within of day of the release of Microsoft’s now notorious chatbot Tay.
Tay mimicked the language patterns of a teenage girl and learnt through her interactions from other Twitter users. However, she became one of the most infamous AI missteps when she started sharing Nazi statements and racial slurs. It turns out that trolls had used the AI’s machine learning against it, flooding it with interactions loaded with bigotry.
Not long after, Microsoft took Tay offline for good.
3. AI Facial Recognition Problems
Facial recognition AI often makes headlines for all the wrong reasons, such as stories about facial recognition and privacy concerns. But this AI also caused huge concerns when attempting to recognize people of color.
In 2015, users discovered that Google Photos was categorizing some black people as gorillas. In 2018, research by the ACLU that showed that Amazon’s Rekognition face identification software identified 28 members of the US Congress as police suspects, with false positives disproportionately affecting people of color.
Another incident involved Apple’s Face ID software incorrectly identifying two different Chinese women as the same person. As a result, the iPhone X owner’s colleague could unlock the phone.
Meanwhile, MIT researcher Joy Buolamwini recalls often needing to wear a white mask while working on facial recognition technology in order to get the software to recognize her. To solve issues like this, Buolamwini and other IT professionals are bringing attention to the issue and the need for more inclusive datasets for AI training.
4. Deepfakes Used for Hoaxes
While people have long used Photoshop to create hoax images, machine learning takes this to a new level. Software like FaceApp allows you to face-swap subjects from one video into another.
But many people exploit the software for a variety of malicious uses, including superimposing celebrity faces into adult videos or generating hoax videos. Meanwhile, internet users have helped improve the technology to make it increasingly difficult to distinguish real videos from fake ones. As a result, this makes this type of AI very powerful in terms of spreading fake news and hoaxes.
To show off the power of the technology, director Jordan Peele and BuzzFeed CEO Jonah Peretti created a deepfake video showing what appears to be former US President Barack Obama delivering a PSA on the power of deepfakes.
5. The Rise of the Twitter Bots
Twitter bots were originally created to automate things like customer service replies for brands. But the technology is now a major cause for concern. In fact, research has estimated that up to 48 million users on Twitter are actually AI bots.
Rather than simply using algorithms to follow certain hashtags or respond to customer queries, many bot accounts try to imitate real people. These ‘people’ then promote hoaxes and help make fake news go viral.
A wave of Twitter bots even influenced public opinion to a degree on Brexit and the 2016 US presidential election. Twitter itself admitted that it uncovered around 50,000 Russian-made bots which posted about the elections.
Bots continue to plague the service, spreading disinformation. The problem is so rife that it’s even affecting the company’s valuation.
6. Employees Say Amazon AI Decided Hiring Men Is Better
In October 2018, Reuters reported that Amazon had to scrap a job-recruitment tool after the software’s AI decided that male candidates were preferential.
Employees who wished to remain anonymous came forward to tell Reuters about their work on the project. Developers wanted the AI to identify the best candidates for a job based on their CVs. However, people involved in the project soon noticed that the AI penalized female candidates. They explained that the AI used CVs from the past decade, most of which were from men, as its training dataset.
As a result, the AI began filtering out CVs based on the keyword “women”. They keyword appeared in the CV under activities such as “women’s chess club captain”. While developers altered the AI to prevent this penalization of women’s CVs, Amazon ultimately scrapped the project.
7. Inappropriate Content on YouTube Kids
YouTube Kids has many silly, whimsical videos meant to entertain children. But it also has a problem of spammy videos that manipulate the platform’s algorithm.
These videos are based on popular tags. Since young children aren’t very discerning viewers, junk videos using these keywords attract millions of views. AI automatically generates some of these videos using stock animation elements, based on trending tags. Even when the videos are made by animators, their titles are specifically generated for keyword stuffing.
These keywords help manipulate YouTube’s algorithm so that they end up in recommendations. A significant amount of inappropriate content appeared in the feeds of children using the YouTube Kids app. This included content that depicts violence, jumpscares, and sexual content.
Why Machine Learning Goes Wrong
There are two major reasons machine learning results in unintended consequences: data and people. In terms of data, the mantra of “junk in, junk out” applies. If the data that is fed to an AI is limited, biased, or low-quality; the result is an AI with limited scope or bias.
But even if programmers get the data right, people can throw a wrench in the works. Creators of software often don’t realize how people may use the technology maliciously or for selfish purposes. Deepfakes came from the technology used to improve special effects in cinema.
What aims to provide more immersive entertainment also ends up ruining people’s lives when exploited.
There are people working towards improving the safeguards around machine learning technology to prevent malicious use. But the technology is already here. Meanwhile, many companies don’t show the required willpower to prevent abuse of these developments.
Machine Learning Algorithms Can Help Us
It may seem a bit doom and gloom when you realize just how much machine learning and artificial intelligence falls short of expectations. But it also helps us in many ways—not just in terms of convenience, but improving our lives in general.
If you’re feeling a bit hesitant about the positive impact of AI and machine learning, find out about the ways artificial intelligence is fighting cybercrime and hackers to restore some hope.
Read the full article: What Are Machine Learning Algorithms? Here’s How They Work
from MakeUseOf https://ift.tt/2zvTLMa
via IFTTT
No comments:
Post a Comment